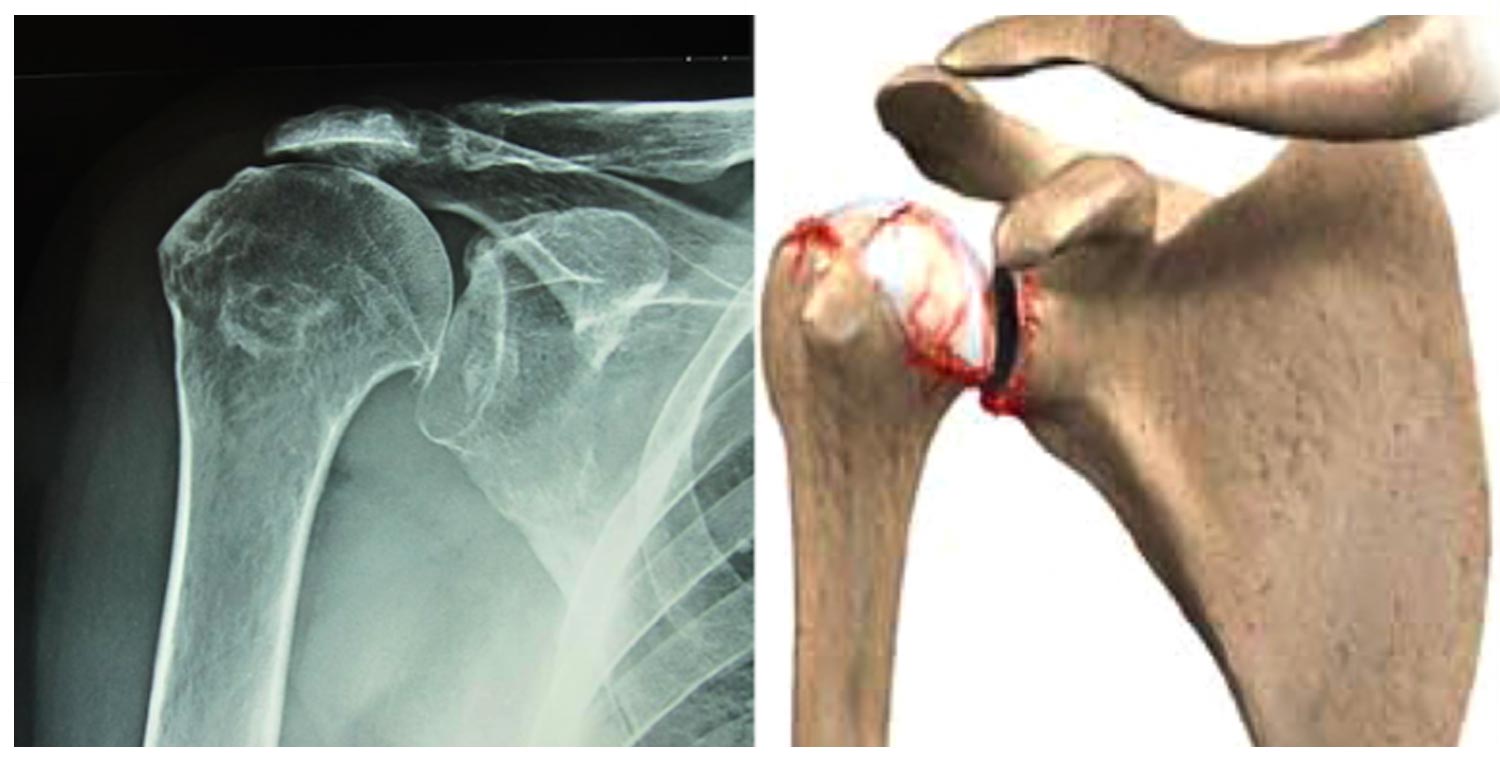
Arthrosis, the third major joint where arthritis occurs after the knee and hip, which is shoulder joint. Shoulder arthrosis (omarthrosis), which commonly known as shoulder calcification, is a progressive disease caused by wear of the cartilage which covering the joint surface. Over time, disruption in the shape of the socket (glenoid) and head (humerus) bones is seen.
Why Shoulder Arthritis occurs?
The simulating cause may be an additional disease (previous shoulder joint infection, rheumatic diseases, bone vascular disorder (Avascular necrosis), chronic rotator cuff rupture, haemophilia), or a previous trauma, or it may occur only with aging without any additional disease.
What Are the Symptoms of Shoulder Arthritis?
Arthritis occurs by wear of the joint. Cartilage cracks, the surface becomes rough. The lubricity of the joint deteriorates, friction increases, along with these, shoulder movements are restricted. Pain increases. Although pain increases from time to time, shoulder pain is most commonly felt at night rest. With rheumatic diseases, swelling and redness with pain in the shoulder may also occur.
How is Shoulder Arthritis Treated?
In the treatment of shoulder arthritis, protective treatments are applied first. Painkiller medications, physical therapy applications, intra-articular injections are applied. Their success rate depends on the degree of arthritis. They are very useful in the early stages. However, patients cannot move their arms due to the increased level of restraint in the forthcoming periods. Studies have shown that young patients who do not have severe arthritis of the joint but whose daily movements are restricted can get benefit from arthroscopic capsular loosening and joint debridement operations.
However, shoulder arthroplasty operations aimed at replacing the joint are an appropriate solution for patients due to increased cartilage damage at advanced arthritis levels.
What is Shoulder Prosthesis?
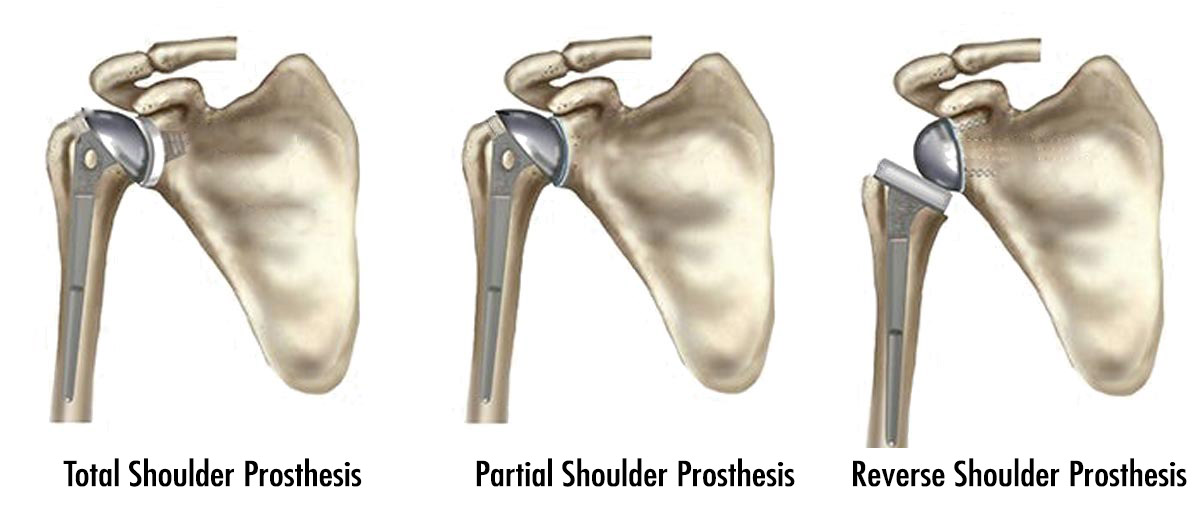
Shoulder prosthesis surgeries provides pain relief of the shoulder along with a comfortable movement. In surgery, the joint surfaces of the problematic shoulder are removed and replaced with smooth metal and plastic surfaces which called prosthesis.
Partial joint replacement (Partial Arthroplasty): If the humeral head is damaged and the glenoid is not damaged, it is only the replacement of the joint surface in the humeral head.
Replacement of the whole joint (Total Arthroplasty): If both humeral head and socket is worn, prosthesis is applied to both surfaces.
Reverse Shoulder Prosthesis: Generally, in advanced ages, if the muscles around the shoulder (rotator cuff) are irreparably torn, a reverse shoulder prosthesis is applied.
Postoperative Process is Important
Exercises that allow the movements of the shoulder joint and strengthen the muscles around the shoulder, directly affect the success of the surgery and the forthcoming process. Therefore, the support of treatment with good rehabilitation increases the success rate. With the support of good surgery and physiotherapy, patients can return to normal activities in 1.5-2 months.