FIRST DAY OF SURGERY
– If spinal anesthesia is performed, the rotation of the leg movements may take 1-4 hours.
– If you have pain and nausea, medication will be given.
– Constipation and inability to urinate may occur due to anesthesia. Say it to your nurse.
– Patients shaking hands with visitors should wash their hands frequently and pay attention to hand hygiene.
– Be careful not to fall into the wet ground in the bathroom and after walking. Don’t get up without help.
– If there is no leaking after the 3rd day, bathing can be done with waterproof dressings.
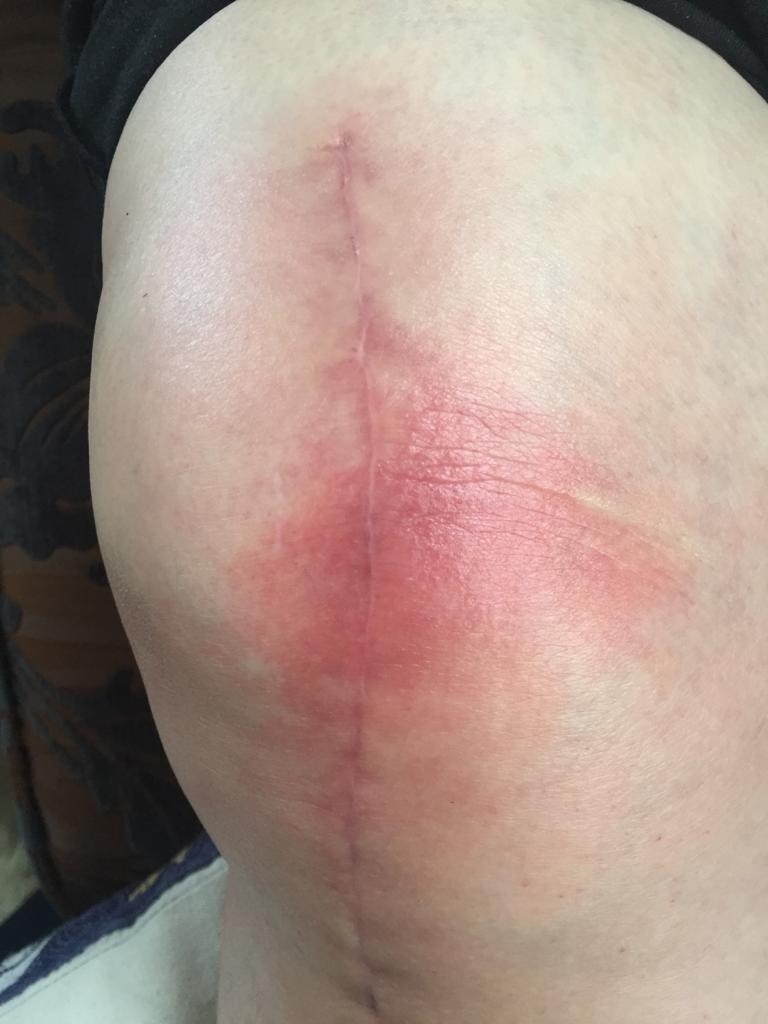
What are the early postoperative problems?
– Swelling, bruising: Swelling may occur at different levels depending on patient in the surgical site. While these swelling decreases, bruising occurs. Over time, these bruises disappear by being yellow.
– Swelling of the leg: In the first month, prolonged sitting by hanging down the leg increases swelling in the leg and foot. Intermittent placement of a pillow under the leg and keeping it high will reduce swelling. Ice, cold shower application, wearing bandages or antiembolic socks reduces swelling. However, tight wrapping of the bandages and leaving the socks folded may cause swelling in lower level. Due to not occur of swelling, exercise is suggested. Resting the leg at high height, if the swelling does not decrease or does increase despite the application of ice, consult to your doctor.