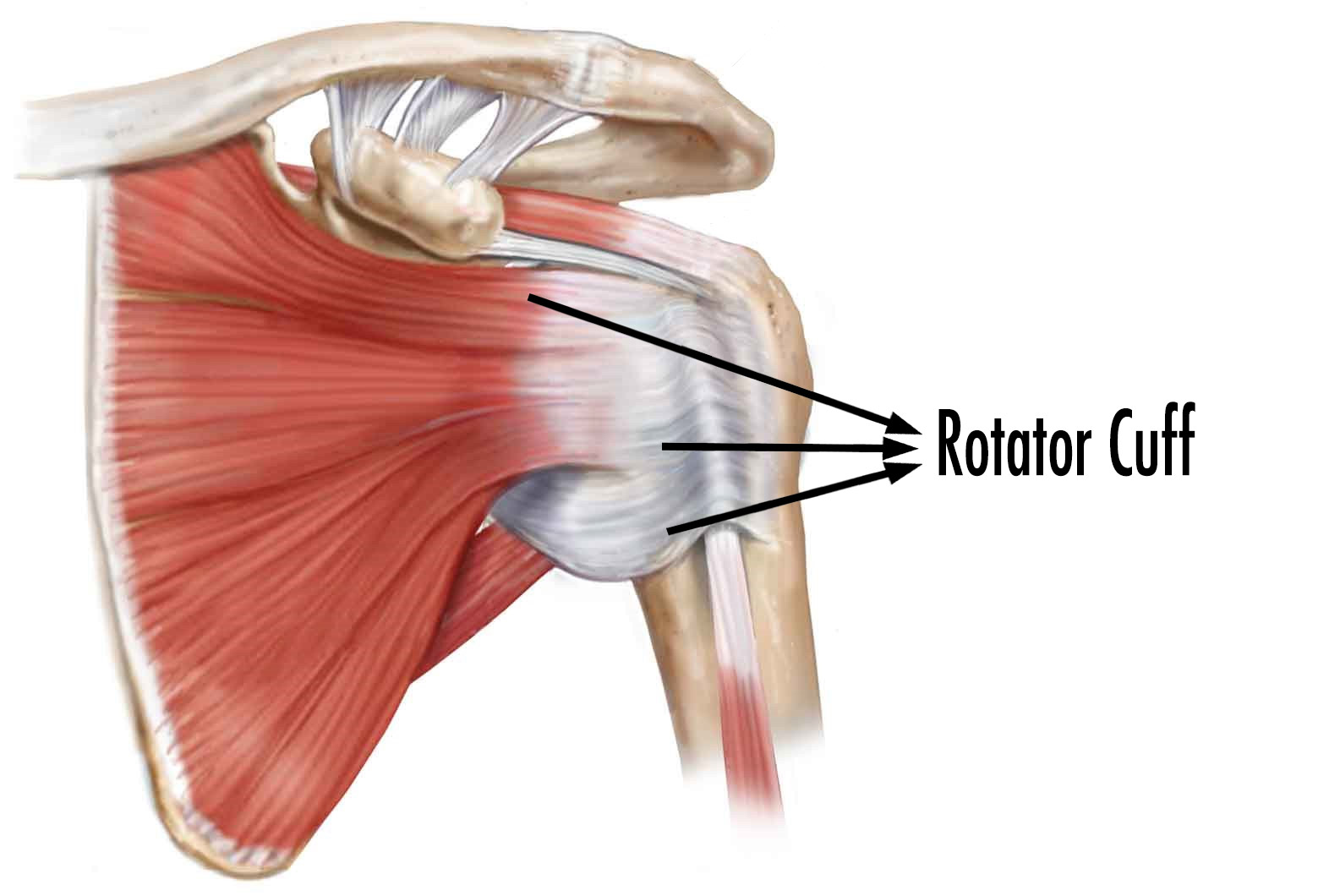
How Shoulder Rotator Cuff Tear is Treated?
Non-surgical or surgical treatment is decided according to the age of the patient and the type of rupture.
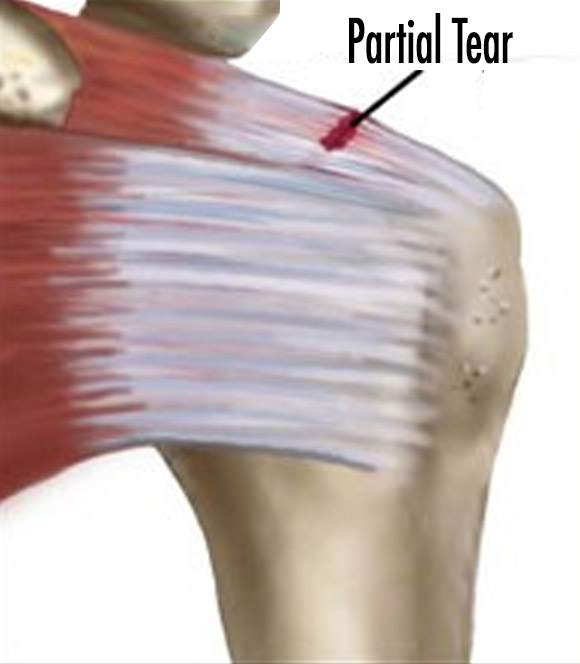
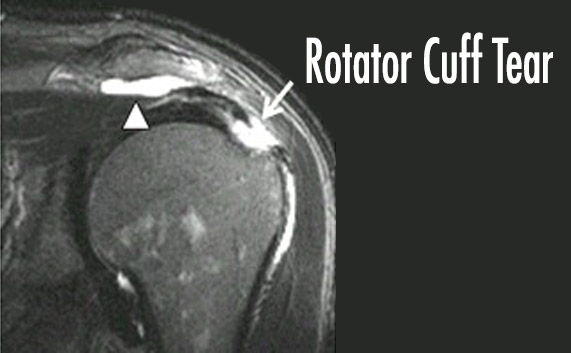
In partial or small tears, pain can be relieved by physical therapy, pain medication, ice treatment and PRP, then the range of motion is increased. All these treatments have no chance of healing. Tear should be followed with MRI controls. If the patient does not relieve pain or increase in tear is developed in MRI, surgical treatment is required.
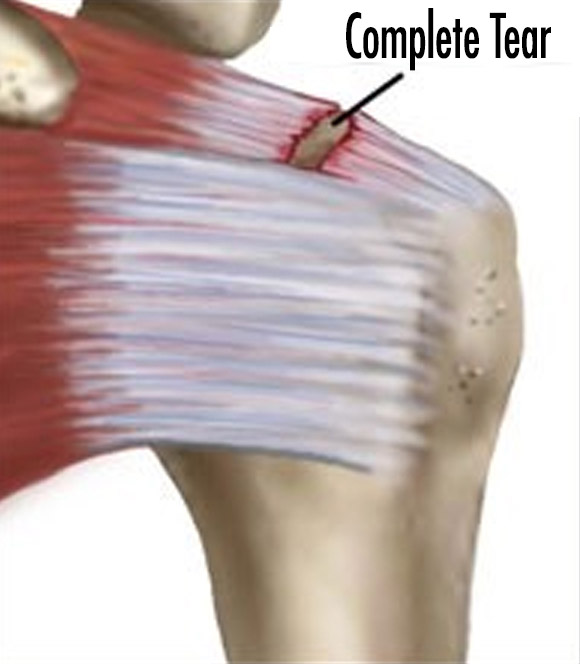
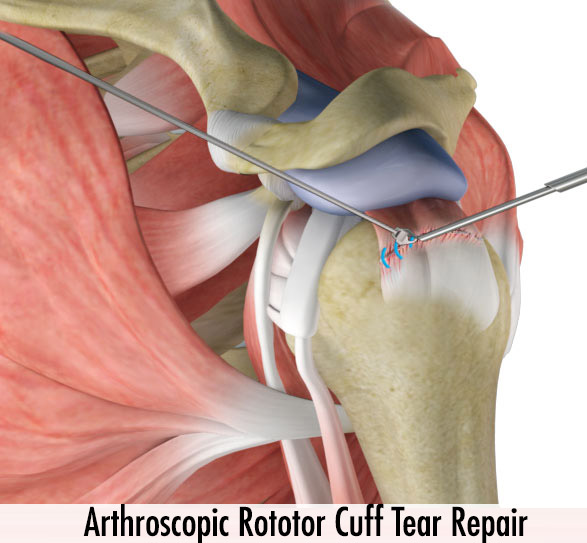
Direct surgical treatment is preferred in patients with; full-thickness tears, young patients, those who do heavy labor for the arm, and patients with loss of strength in the arm. Because the tear which doesn’t be sutured will grow in time. In fact, if the tear is not repaired for a long time, unused muscle gains fat and lose its function over time. In this case, as the sutured muscle will not function, also the tear may be torn again in the early postoperative period.
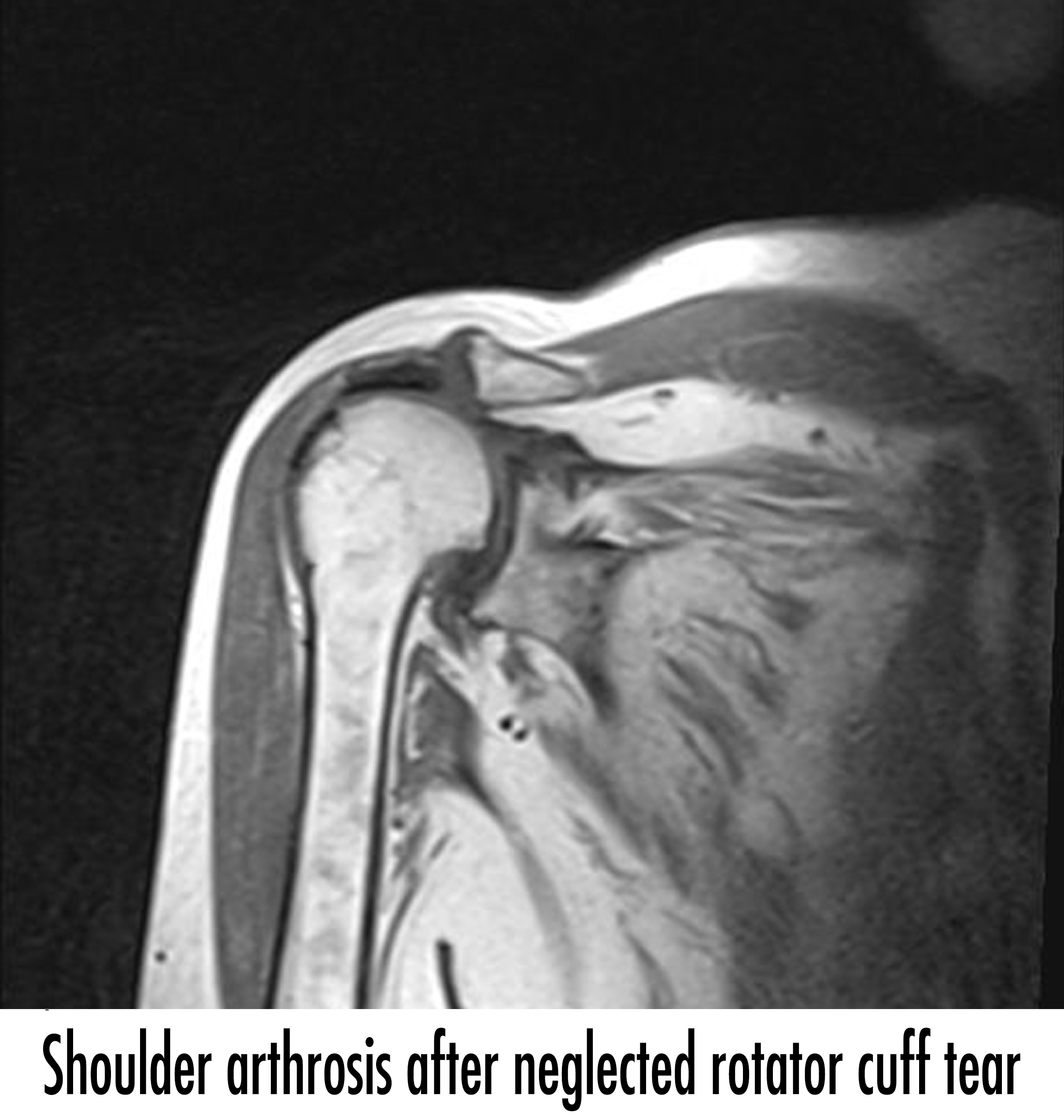
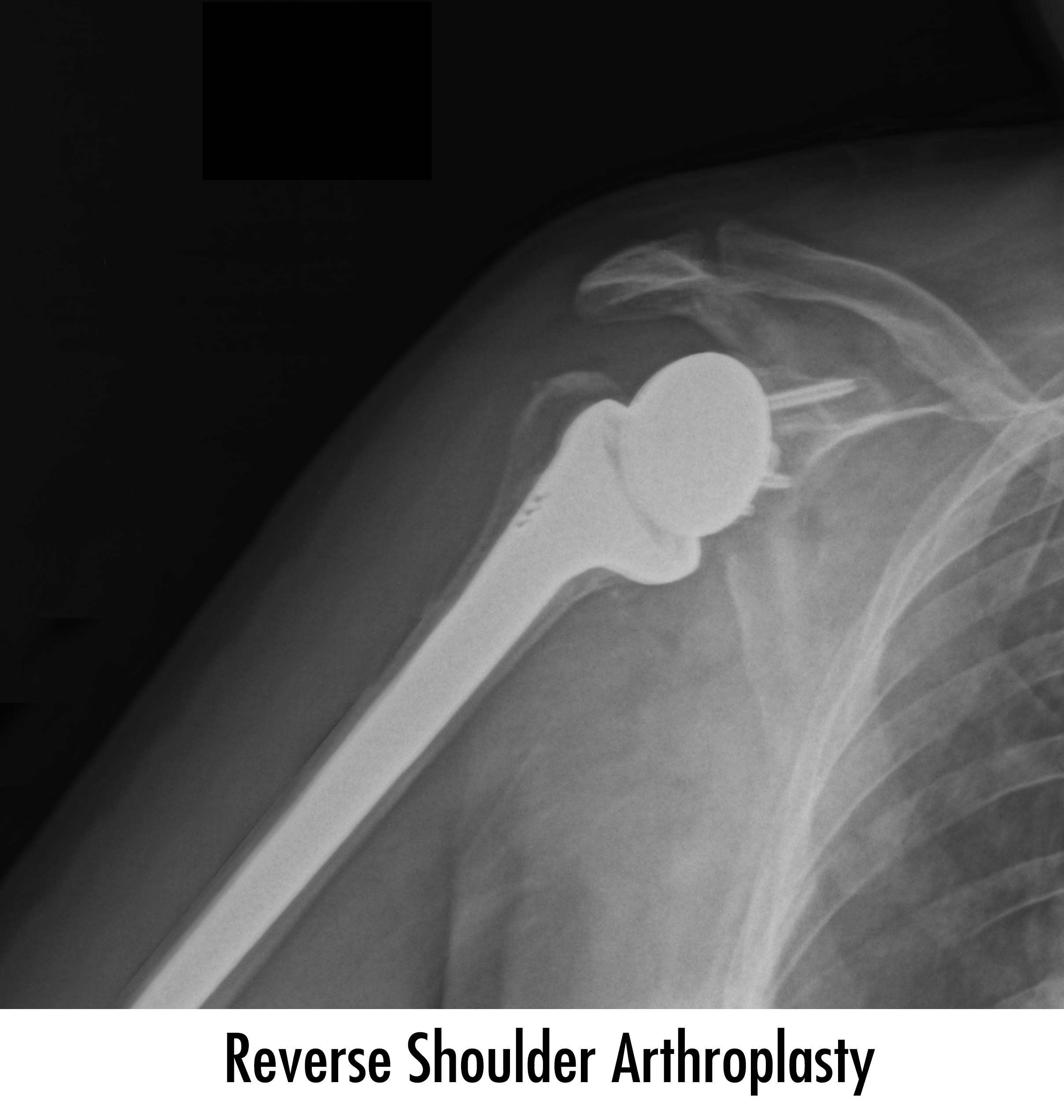
Depending on the age and activity of the patient, surgical treatment can be performed as closed surgery in the form of arthroscopic repair or as open surgery as tendon transplantation. If the patient age with advanced and neglected muscle tears that have no chance of repair,and if there is pain in shoulder, shoulder prosthesis may be preferred. Shoulder prosthesis can relieve pain, even though movements are not exactly as before.