How is anterior cruciate ligament rupture treated? Is non-surgical treatment possible?
ACL surgery is required if there is insecurity such as knee; gliding, gapping, or instability. Anterior cruciate ligament surgery is also essential, especially in young patients with this type of complaint. In scientific researches; In patients who hasn’t treated anterior cruciate ligament tear, X-ray taken at the end of the 10th year and arthritis findings are seen in 53% of the patients. If the anterior cruciate ligament injury is repaired in a timely and good way, as a result of fixing the knee instability problem, protective effect will be obtained against meniscus and cartilage injuries. Therefore, contrary to popular belief; Surgical treatment is the best choice for functional outcomes.
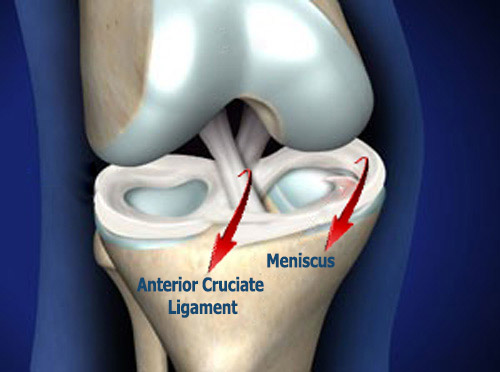
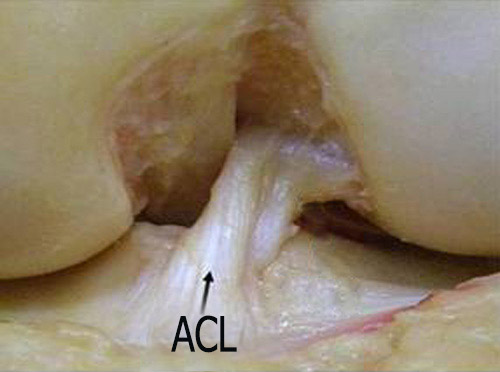
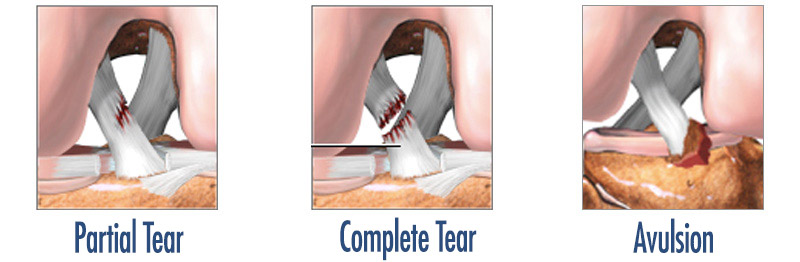
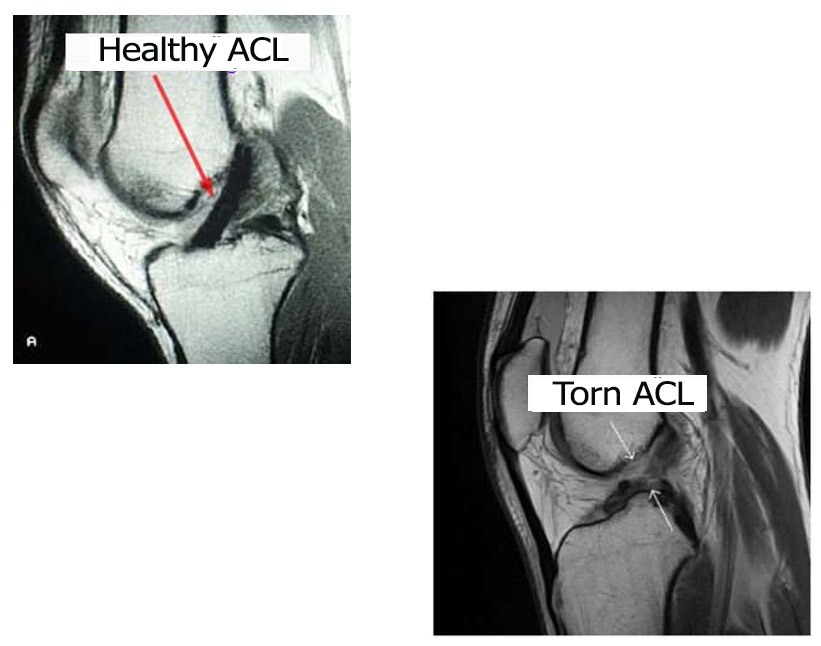
The anterior cruciate ligament, which connects the two bones that make up the knee joint, is overloaded during trauma and breaks by fraying. In addition, the anterior cruciate ligament, which is subjected to excessive stretching by unstable knee motion, does not heal by itself. Because of these reasons, the treatment of anterior cruciate ligament is surgical. Accompany of meniscus tear should be suspected in ACL injuries, if there is a complaint of pain and lockup. Only in children, the anterior cruciate ligament breaks from the bone attachment with the bone fragment and must be sutured in the early stage (first 3 weeks) with a special technique.
Nowadays, anterior cruciate ligament surgeries are performed by arthroscopy, so as closed method. The original ligament is replaced with ligaments (such as hamstring, patellar tendon) from different parts of the body. Ligaments from the cadaver can also be used.
Non-operative treatment may be preferred by exercising the muscles around the knee and keeping muscles strong in patients over 50 years of age, who do not engage in active sports and who doesn’t meet findings of knee gap or knee arthritis.
When do I get up after ACL surgery?
Postoperative hospital stay is 2 days. The knee movements start on the same day. Postoperatively, bearing has to be started with crutches as much as the pain can be tolerated. You need to protect the knee from overloads using crutches 3 weeks and a long knee brace with hinged crutches for 6 weeks postoperatively, on average. There is a great benefit in the rehabilitation of the patient under the guidance of a physiotherapist. With the postoperative exercise program, knee movements are gained almost in three weeks.
When can I drive after ACL surgery?
Patients can use the automatic cars after the left knee surgery when they feel comfortable, but they can drive 6 weeks after the right knee surgery.
When can I return to work after ACL surgery?
Desk employees can return to work in 3-4 weeks. Those who work with their body can return to their jobs between 6 and 9 weeks.
When can I start sports after ACL surgery?
The improvement in ACL surgery varies depending on person. The reasons of this are; patient’s adequacy of muscle strength, age, type and location of used ligament, strength of ligament fixation, technique of surgical procedure and other causes accompanying injury. Generally, patients perform closed kinetic chain movements during the first 6 weeks, while open kinetic chain movements such as cycling and swimming are started after 6 weeks. After 3 months, patients can run straight. However, it is usually possible to start sports training after 6 months due to the ligament has reached its sufficient strength. It takes a year for the tissue to fully mature and firm. Therefore, it is recommended to start sports with contact after 9-12 months.
What is the success rate of ACL surgery?
The success rate in the world and in our country is around 80-90%.
What are the causes of ACL surgery failure?
Failure rate is between 10-20% and the reasons are as follows:
1. Failure of the patient to participate in rehabilitation by acting incompatible with treatment
2. Not enough thickness of placed ligament
3. Improper opening of the tunnels during surgery
4. Incomplete fixation
5. Elongation or re-rupture of the inserted ligament
6. Development of infection
What are the complications of ACL surgery?
- Joint stiffness: Inflammation of the knee (edema) develops in the early post-traumatic rotation. If there is no ligament and meniscus damage other than ACL injury, surgery should not be performed during this period. If the anterior cruciate ligament surgery is performed before knee movements are gained which after edema period is over, joint stiffness may develop in the knee.
- Vascular nerve damage:as a result of damage to the skin nerves by skin incision, deadness feeling may develop on skin. Large vessel nerve injuries are very rare.
- Tendon graft failure
- Disorders where the tendon graft is taken: such as pain, swelling, bruising
- Reflex sympathetic dystrophy: This condition’s reason is not fully understood and is a very rare complication that can cause excessive pain and joint stiffness (even after minor injuries).